Understanding Types Of Foundations For Adus In San Francisco
When contemplating the addition of an Accessory Dwelling Unit (ADU) to a property in San Francisco, one crucial aspect to consider is the selection of an appropriate foundation type.
This article delves into the three primary types of foundations commonly used for ADUs: crawlspace, slab, and basement foundations. It discusses essential factors to take into account when choosing a foundation and constructing ADUs on existing foundations.
Additionally, the piece provides insights into the permitting and zoning prerequisites applicable in San Francisco. It aims to furnish readers with information on how to optimize the potential of their ADU projects.
What are ADUs?
Accessory Dwelling Units (ADUs) are supplementary residential spaces on a property that function independently from the primary dwelling unit. In San Francisco, ADUs present homeowners with the opportunity to expand the housing options available on their property.
These ADUs manifest in various configurations, including detached structures such as standalone tiny houses, repurposed garages, or basement apartments. They afford homeowners the flexibility to accommodate multigenerational families, generate rental income, or offer housing for caregivers.
The capacity to establish ADUs plays a pivotal role in addressing the housing inadequacy in San Francisco by optimizing the use of existing space, thereby obviating the necessity for extensive development endeavors. This approach fosters a more sustainable and financially prudent method of meeting the city’s housing requirements.
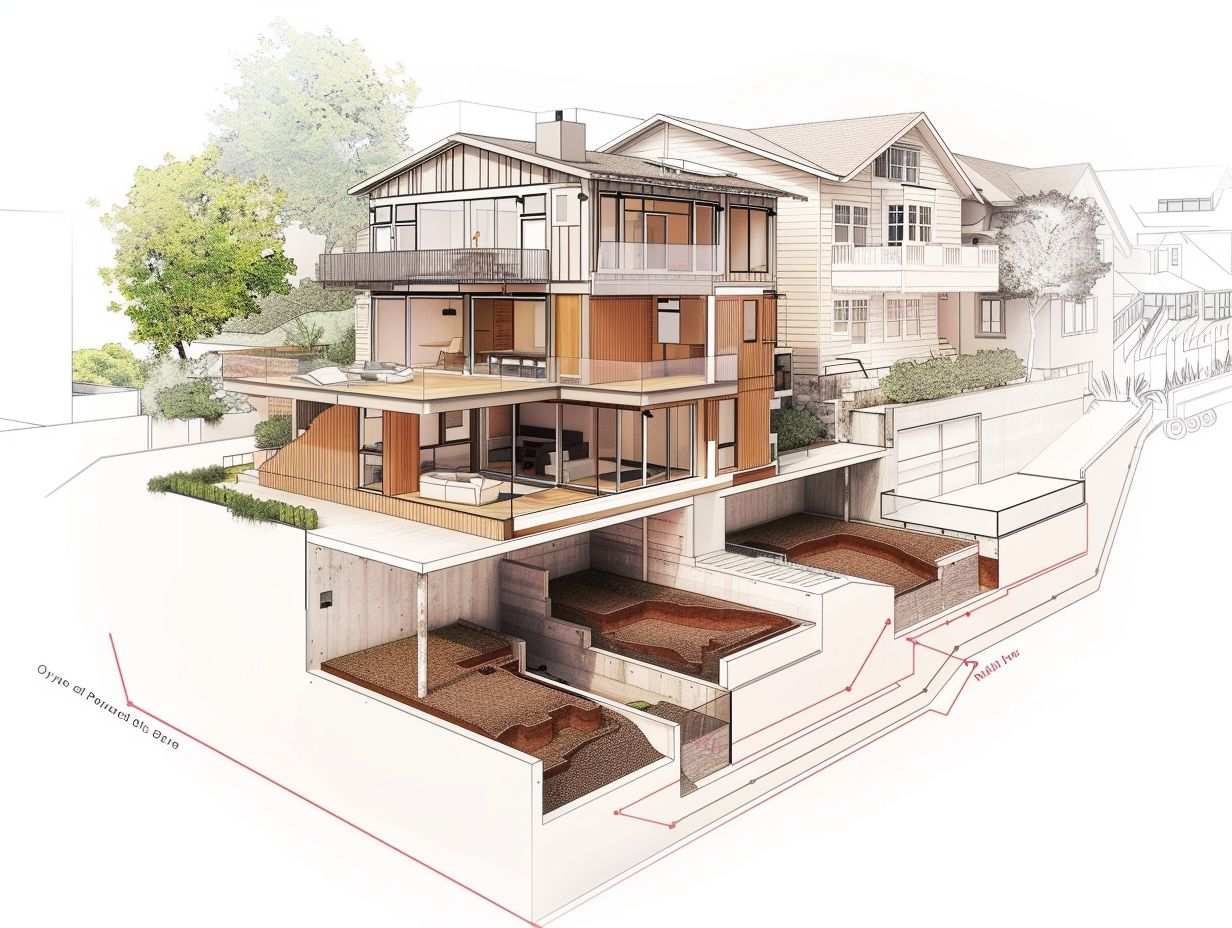
Types of Foundations for ADUs
When developing Accessory Dwelling Units (ADUs), the selection of an appropriate foundation type is essential to guarantee the structural integrity and durability of the supplementary living area. The choice of foundations for ADUs may vary depending on the particular demands and limitations of the property.
Crawlspace Foundations
Crawlspace foundations for Accessory Dwelling Units (ADUs) entail the establishment of a raised foundation that provides access to the underside of the structure. This approach is particularly suitable for properties facing specific soil conditions or space constraints. It is imperative for contractors to strictly comply with building codes to uphold the structural integrity of the ADU.
Such foundation types offer distinct advantages for properties where conventional foundation options are not viable due to challenging soil conditions or restricted space availability. Opting for a crawlspace foundation enables property owners to address the complexities associated with constructing on sites characterized by poor soil drainage or uneven terrain.
The utilization of this method facilitates the easier installation of utilities and insulation beneath the structure, thereby improving energy efficiency and reducing long-term maintenance expenses. Engaging experienced contractors from the project’s inception is essential for successfully navigating the intricate process of constructing a crawlspace foundation that is in full adherence with building regulations and aligns with the property’s specific requirements.
Slab Foundations
Slab foundations for Accessory Dwelling Units (ADUs) entail the utilization of a solid concrete base that is directly poured onto the ground surface. This method provides a robust and economically viable solution for construction projects. The excavation process and acquiring the necessary permits are pivotal stages in the implementation of slab foundations for ADUs.
The structural integrity of slab foundations is derived from their capacity to evenly distribute weight across the ground, thereby diminishing the likelihood of settlement or displacement over time. This attribute renders slab foundations a dependable choice for ADU construction, ensuring enduring stability.
The cost-efficiency of utilizing slab foundations stems from their streamlined construction procedure, which results in reduced material and labor expenses. Excavation is essential for preparing the construction site for the slab foundation, ensuring a level surface and adequate drainage. The permitting process involves securing approvals to comply with pertinent building codes and regulations, thereby safeguarding the structural soundness of the ADU.
Basement Foundations
The establishment of basement foundations for Accessory Dwelling Units (ADUs) involves the utilization of existing space or the creation of a new basement area to accommodate the additional living unit. This process provides opportunities for retrofitting and property upgrades. The design of basement foundations is paramount to ensure the structural integrity of the ADU.
It is essential for homeowners to carefully select appropriate materials and structural designs for the basement foundations to guarantee that they can support the weight of the ADU while enduring environmental factors and potential ground movements. Retrofitting basement foundations for ADUs can enhance the property’s value, thereby increasing its overall appeal and functionality.
Properly planned basement foundations not only offer stability for the ADU’s structure but also contribute to energy efficiency and the overall comfort of the living space. Investing in well-designed basement foundations is crucial for the long-term success and sustainability of ADUs.
Factors to Consider When Choosing a Foundation Type
Numerous factors must be taken into account when choosing a foundation type for Accessory Dwelling Units (ADUs), including soil conditions, cost estimations, and permitting fees. These considerations are crucial in assessing the feasibility and ensuring the success of the ADU construction project.
Soil Conditions and Building Codes
The consideration of soil conditions and adherence to building codes are crucial factors to contemplate when strategizing the foundation for Accessory Dwelling Units (ADUs). The initiation of a geotechnical report serves to evaluate the properties of the soil and ensure alignment with regulatory standards for the purpose of constructing in a safe manner.
It is imperative to recognize that the stability and longevity of any edifice, including ADUs, are significantly reliant upon the caliber of the foundation that is established. Thorough geotechnical reports offer pivotal insights into soil composition, bearing capacity, and potential hazards, such as settlement or erosion. Adhering rigorously to building codes ensures that homeowners and builders not only certify the structural soundness of the ADU but also guarantee the safety of its inhabitants. The adherence to these regulations constitutes a fundamental stride in fostering a secure and resilient living atmosphere within the premises.
Cost and Construction Time
The consideration of cost and construction time holds significant importance when selecting a foundation type for Accessory Dwelling Units (ADUs). Accurate cost estimation, effective management of construction schedules, and a thorough understanding of permitting expenses are critical factors that influence the overall project budget and financing alternatives.
A comprehensive cost analysis allows individuals to assess the financial viability of different foundation types, ensuring adherence to budgetary constraints. Efficient construction timelines play a vital role in preventing delays and mitigating additional expenditures. Adequate management of permitting costs not only results in cost savings but also optimizes the overall building process. When evaluating financing options, it is essential to explore diverse avenues such as loans, grants, or partnerships to secure comprehensive coverage for the ADU project.
Building ADUs with Existing Foundations
In certain instances, the construction of Accessory Dwelling Units (ADUs) utilizing existing foundations may present a feasible option, necessitating retrofitting and structural assessments conducted by qualified engineers. The incorporation of green building practices and verification of the accessory structure’s compatibility are pivotal considerations in the execution of such projects.
Assessing the Viability of Existing Foundations
The evaluation of the adequacy of current foundations for Accessory Dwelling Units (ADUs) requires a meticulous inspection of the structural soundness, potential retrofitting prerequisites, and collaboration with structural engineers to guarantee safety and adherence to building regulations.
Before commencing any construction or refurbishment activities on an existing foundation, it is imperative to undertake a comprehensive evaluation process. This assessment typically encompasses a thorough examination of geotechnical reports, which furnish crucial information on soil conditions and possible hazards. Structural engineers are pivotal in this phase, bringing their expertise in foundation design to the table and appraising the structural capacity of the current foundation. Retrofitting, where deemed necessary, can fortify the foundation’s capability to sustain additional loads and ensure enduring stability for the ADU framework. By methodically adhering to these steps, property owners can establish a robust foundation for their ADU project.
Permitting and Zoning Requirements for ADUs in San Francisco
Successfully navigating the permitting and zoning requirements for Accessory Dwelling Units (ADUs) in San Francisco necessitates a comprehensive comprehension of the legal framework, adherence to zoning regulations, and acquisition of approvals from the local Planning Department. Adhering to these rigorous requirements is imperative for the successful completion of ADU construction projects.
Understanding the Process and Requirements
Understanding the permitting and zoning process for Accessory Dwelling Units (ADUs) in San Francisco entails compliance with residential zoning regulations, participation in affordable housing programs, and adherence to retrofit ordinances. Acquainting oneself with the stipulated requirements is imperative for effectively navigating the regulatory landscape.
Navigating the complexities associated with obtaining permits and adhering to zoning regulations in San Francisco is paramount for individuals seeking to develop ADUs. Apart from adhering to residential zoning regulations, active engagement in affordable housing programs, such as the Affordable Housing Program, is essential to ensure that the construction and rental of ADUs align with the city’s objectives regarding housing affordability. Furthermore, a thorough understanding and adherence to retrofit ordinances are equally critical, as these regulations are designed to enhance the safety and functionality of ADUs in alignment with city standards.




No Comments